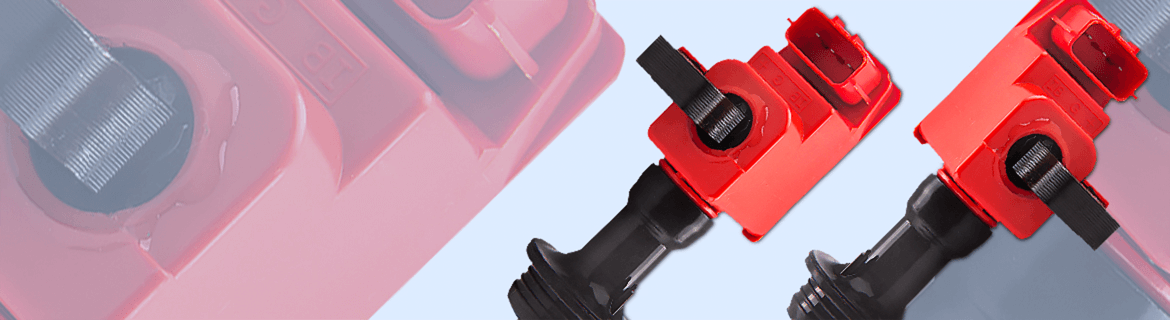
Ignition Coils Buyer's Guide
Buying an ignition coils for your car can sometimes be a daunting and confusing task. At maxpeedingrods.com, it is our mission to make that task as an easy and painless as possible. This Buyer's Guide is designed to answer any questions you may have during your search for the right ignition coils for your car, and how to buy ignition coils on our website.
What is an ignition coil and how does it work?
In an internal combustion engine, 'ignition' refers to the process wherein a spark produced by the spark
plug triggers an explosion and ignites the air-fuel mixture required to power the engine. The ignition
system consists of several components, namely ignition coil, spark plug, distributor, rotor, etc. Each
of these are assigned a specific function in the engine's overall working mechanism. While the spark
plug creates a spark required to trigger the explosion of fuel-air mixture, the distributor distributes
this spark to the appropriate spark plug.
The power that the 12-volt battery used in the machine tends to produce is insufficient to trigger the
spark necessary to facilitate explosion, which is where the 'ignition coil' comes into the picture. It
converts the battery's 12-volt power into 40 kV power required to create the spark. In other words, it
is an induction coil, which converts the relatively weak power from the battery to enormous
power―amounting to 40 kV―that is required to produce the spark which ignites the air-fuel mixture in the
ignition system.
The current from the battery begins building up when the contact breaker closes, and continues until it
reaches its full capacity. Once it reaches its full capacity, the contact breaker opens and the high
voltage spark is produced. If the ignition coil is not there, the 12v DC battery on board the vehicle is
of no use, as such little amount of power is not sufficient for creating the spark that's required to
produce the explosion.
While some of these coils resort to resistor to reduce the voltage,
others rely on a resistor wire or an external resistor to facilitate the same.
Basically, the ignition coil is made up of two coils of wire―placed one on the top of other. These coils
are also referred to as windings, with the first coil being referred to as the 'primary coil', while the
second coil, which is wrapped around the primary coil, being referred to as the 'secondary coil'. The
number of turns in secondary coil is in multiples of the number of turns in its primary counterpart. The
current flows from the battery through the primary coil, wherein it is collected together to produce the
required spark, which is eventually sent to the distributor by the secondary coil.
In order to make sure that the tremendous amount of heat generated in this process doesn't harm the
coil, it is filled with oil which acts as its coolant. While some engine models are equipped with a
single ignition coil, others have one for each spark plug. In models with single spark plug, a
distributor is used to distribute the spark to the appropriate spark plug.
Of the various ignition problems that you are likely to face, weak spark and coil not firing are the
ones that are attributed to the ignition coil. In order to diagnose these problems, you can either
resort to the spark plug test or the bench test. That will help you determine whether you need to
replace it.
How to choose ignition coils?
Ignition coils operate in a very similar fashion to a transformer; with a 12-volt power source that
produces output current simultaneously to an input current that's being applied. By creating an
efficient magnetic field, the force of the electricity is multiplied from the battery source – thus
allowing your engine to ignite quickly. Different engines have specific ignition system specs geared
towards optimizing engine performance while keeping fuel economy top of mind. With long-term usage,
stock ignition coils will require replacement; and you can get the efficiency of your system back by
immediately fixing your ignition coil at the first sign of failure.
Ignition coils are critical to the working of your vehicle, quickly converting the very low energy of a
battery into the thousands of volts of energy required to produce ignition in your car. Without this
critical piece of equipment, you would be required to push your car in order to get it to ignite. Fuel
efficiency and overall engine performance are compromised when you continue using an ignition coil that
has gone bad, so replace them at the first sign of a problem. Here are some tips to ensure that you have
the best long lasting ignition coils:
• Invest in a premium quality ignition coil to ensure quick ignition: this is the best solution to
high-quality engine performance.
• A heavy-duty ignition coil provides miles and miles of extra service and a much longer and more
efficient lifecycle.
• You can purchase street or strip ignition coils that work best for race cars and are rated up to
55,000 volts, providing significantly better performance than stock ignition coils. They offer better
throttle response, improved gas mileage and quicker and easier starts.
Know the details about your vehicle's distributor, as this may limit your choices at the parts store.
Why buy ignition coils at MaXpeedingRods?
MaXpeedingRods has been engaged in the research of overseas racing products and culture for
decades. If you are looking for ignition coils, you have landed at the right place. On the basis
of your vehicle make and model, you can choose from a plethora of automotive maintenance and
accessories. MaXpeedingRods offers a seamless online shopping experience and the streamlined
e-commerce interface makes it easy for you to find just the ignition coil you want.
MaXpeedingRods offers a variety of ignition coils with high quality.
• Increased Ignition Performance— High voltage output and spark energy
• Improved Combustion
• Possible power increase of around 11KW(15hp) at the wheels
• Improved throttle response and smoothness
• No spark blowout at higher boost • Direct fit for factory mountings
• Solid construction
• Performance aftermarket parts in 100% brand new

What are the symptoms of an ignition coil failure?
If your vehicle is behaving erratically and you have problems with it running smoothly, it could be showing signs of ignition coil failure. The ignition coil takes power from the generator and relays it to the spark plugs. This ignites the fuel and makes your vehicle run. The severity of the symptoms vary according to which of the ignition coils are failing.
If your vehicle is backfiring, this can indicate early symptoms of an ignition coil failure. This occurs when unused fuel is emitted through the exhaust system. If you do not address the issue, you can also do serious damage to your exhaust, resulting in unnecessary and costly repairs. Your exhaust may emit a black smoke and you may even detect the smell of gasoline.
2. Starting ProblemsCheck your high tension leads (HT Leads). They run between the distributor and spark plugs. Ignition coil failures result in 1 or more spark plugs not receiving the appropriate amount of charge. If you have trouble starting your vehicle in the cold, this is a good sign of potential ignition coil failure. You can run a simple test on the HT leads to check that there is in fact a spark going from each lead to each spark plug.
3. Fuel EconomyIf your vehicle is getting a lot less mileage for the gallon, it could also be a sign of an ignition coil failure. When less power is reaching the spark plugs, your vehicle will struggle and use more fuel to compensate for the lack of power transfer.
4. Engine MisfiringTrying to start your vehicle when the ignition coils fail will result in a rough ride. Your vehicle will cough and splutter regularly. When you drive at high speeds, your vehicle will jerk and spit. It will also vibrate when you are running idle at a stop sign or intersection.
5. Vehicle StallingWith ignition coil failure, your vehicle will have irregular sparks emitting to the plugs to keep it running. This will result in stalling. When you bring your vehicle to a stop, it may just shut off totally, thus leaving you needing to restart it.
6. Coil FailureIf your spark plugs are worn out, it forces the ignition coils to operate at a much higher output. Keeping your sparks plug in optimum condition can reduce your chances of experiencing an ignition coil failure. Some simple regular maintenance will save you a lot of money in the long run. If the gap in your spark plug widens due to normal erosion, it leads to an increased voltage being required to create a spark in the chamber. The increased voltage demands more current flow through the primary circuit and this increased current flow can overload the primary transistor. Keeping all these components in good running condition is also a big help towards keeping your coils in a good working condition.

How to install ignition coils in a car?
Do you have intermittent spark and a "check engine" light for the ignition coil or misfire?
We can help you with that. Multiple ignition coil packs look intimidating for those used
to the traditional distributor and single coil, but they are just as easy to replace.
Step 1: Remove the negative battery cable.
Step 2: Locate coil packs or ignition coil in the engine bay. If your car has a distributor, follow the
wire that is in the center of the distributor cap to find the igniton coil. Cars with coil packs usually
have them mounted near a valve cover. Coil on plug ignition coils are typically placed near or directly
over each spark plug. Remove any plastic engine covers or air intake tubes to gain access to the coils.
Step 3: Unplug the wiring harness by pushing the tab and pulling off the electrical connector.
Step 4: Remove the retaining bolts holding the coil in place. Once unbolted, the coil pack can be easily
pulled out of the engine now, but be aware that some models have a locking tab that needs to be opened.
Step 5: If it is time to change the spark plugs, do that now.
Step 6: Apply dielectric grease inside the end of the coil-on-plug style, as this prevents the boot from
sticking to the spark plug and helps keep water out of the connection.
Step 7: Slide the coil into place, pressing firmly so the boot clicks onto the spark plug. Reattach the
electrical connection and the coil pack retaining bolt.
Step 8: Proceed to the next coil pack until all units have been replaced. Finally, reconnect the
negative battery cable.


 (1) 213-459-3517
(1) 213-459-3517